Overview
Volume Based Routing allows you to distribute payment transactions across multiple processors using predefined percentage allocations. This strategy helps balance transaction loads, optimize costs, manage risk, and maintain redundancy in your payment processing infrastructure.Key Benefits
- Load Distribution: Spread transaction volume across multiple processors
- Risk Management: Avoid over-reliance on a single payment processor
- Cost Optimization: Balance processing fees by leveraging different processor rates
- Performance Management: Maintain optimal processing speeds by distributing load
- Redundancy: Ensure continued operations if one processor experiences issues
How Volume Based Routing Works
The system automatically distributes incoming transactions according to your configured percentage splits. For example:- Processor A: 60% of transactions
- Processor B: 30% of transactions
- Processor C: 10% of transactions
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Access Volume Based Configuration

- Navigate to the Smart Router section in your dashboard
- Locate Volume Based Routing in the routing options
- Click on Setup to begin configuring Volume Based routing
Step 2: Define Rule Details
 Rule Information:
Rule Information:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for your volume routing rule
- Example: “Primary Volume Distribution” or “Q1 2024 Volume Split”
- Description: Add a detailed description of the rule’s purpose
- Include business rationale and expected outcomes
- Note any specific conditions or timeframes
Step 3: Configure Volume Distribution
 Processor Allocation:
Processor Allocation:
- Select Processors: Choose which payment processors to include in the distribution
- Set Percentages: Assign percentage values to each processor
- Validation: Ensure total percentages equal 100%
- Preview: Review the distribution before saving
Step 4: Save and Activate
 Completion Options:
Completion Options:
-
Save Rule Only:
- Saves the configuration without activating
- Useful for preparing rules for future use
- Allows testing and validation before going live
-
Save and Activate:
- Immediately applies the rule to all incoming payments
- Replaces any currently active volume routing
- Starts distributing transactions according to new percentages
Step 5: Monitor and Manage
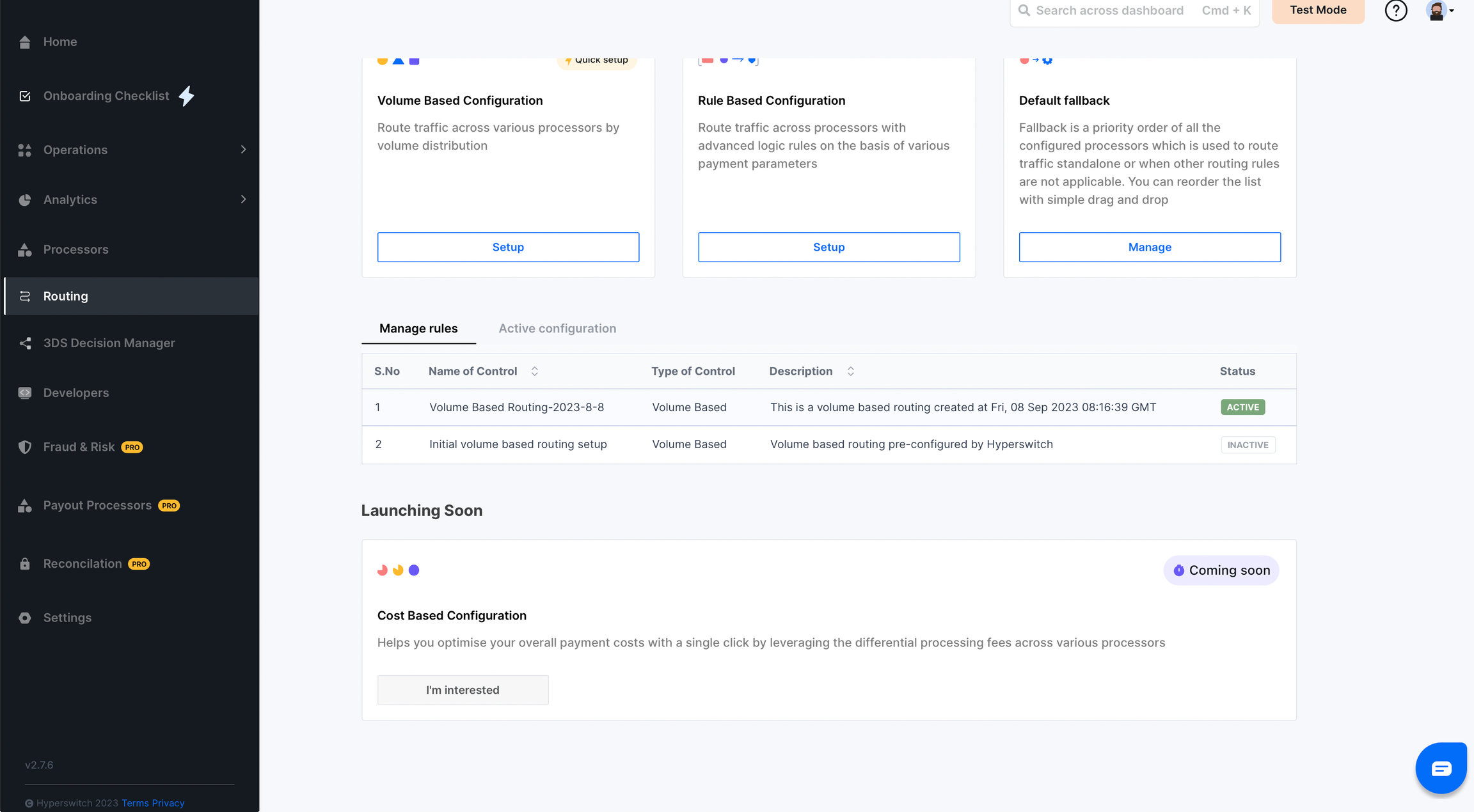 Dashboard Overview:
Dashboard Overview:
- Active Algorithm: View currently active volume routing configuration
- Historical Rules: Access all previously configured routing algorithms
- Performance Metrics: Monitor distribution effectiveness and processor performance
Best Practices for Volume Distribution
Strategic Allocation
Primary Processor (Highest %)- Choose your most reliable and cost-effective processor
- Typically handles 40-60% of volume
- Should have excellent uptime and support
- Allocate 20-40% based on specific strengths
- Consider geographic expertise or payment method specialization
- Balance cost with performance requirements
- Usually handles 5-20% of volume
- Serves as redundancy and testing ground
- Can be used for new processor evaluation
Common Distribution Strategies
| Strategy | Primary | Secondary | Backup | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 70% | 25% | 5% | Stable, proven processor focus |
| Balanced | 50% | 35% | 15% | Even distribution for risk management |
| Experimental | 40% | 40% | 20% | Testing new processors or markets |
| Cost-Optimized | 60% | 30% | 10% | Lowest-cost processor priority |
Advanced Configuration Options
Conditional Volume Routing
Enhance basic volume routing with additional conditions: Payment Method Specific:- Different volume splits for cards vs. digital wallets
- Separate distributions for credit vs. debit cards
- Regional processor preferences
- Local vs. international transaction handling
- Different splits for high-value transactions
- Micro-payment vs. standard payment routing
Time-Based Variations
Business Hours vs. Off-Hours:- Adjust processor allocation based on time of day
- Route to processors with better 24/7 support during off-hours
- Modify volume distribution for peak shopping periods
- Increase allocation to processors with better high-volume handling
Monitoring and Analytics
Key Performance Indicators
Distribution Accuracy:- Target vs. Actual: Compare intended percentages with actual distribution
- Volume Variance: Track deviations from planned allocation
- Time Period Analysis: Monitor distribution over different timeframes
- Success Rates: Compare performance across different processors
- Processing Times: Analyze speed differences between processors
- Cost Analysis: Track total processing costs by processor
Dashboard Metrics
Real-Time Monitoring:- Current distribution percentages
- Transaction counts by processor
- Success rate comparisons
- Cost summaries
- Weekly/monthly distribution reports
- Processor performance trends
- Cost optimization opportunities
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Uneven Distribution- Cause: Low transaction volume may cause temporary imbalances
- Solution: Monitor over longer time periods for accurate distribution
- Prevention: Consider minimum transaction thresholds for activation
- Cause: One processor experiencing outages or high failure rates
- Solution: Implement automatic failover to maintain service
- Prevention: Set up monitoring alerts for processor performance
- Cause: Configuration errors or system bugs
- Solution: Verify configuration and contact support if needed
- Prevention: Always validate percentages total 100% before saving
Performance Optimization
Regular Review Schedule:- Weekly: Check for any significant deviations from target distribution
- Monthly: Analyze processor performance and cost effectiveness
- Quarterly: Review and adjust percentage allocations based on business needs
- Increase allocation to best-performing processors
- Decrease allocation to processors with high failure rates
- Adjust based on seasonal business patterns
Integration with Other Routing Rules
Hierarchical Routing
Volume Based Routing can work alongside: Primary Rules:- Geographic routing takes precedence
- Payment method routing overrides volume rules
- Risk-based routing for high-risk transactions
- Volume routing applies when primary rules don’t match
- Default fallback handles cases where volume routing fails
Rule Priority Management
- Geographic Rules: First priority for location-specific requirements
- Payment Method Rules: Second priority for method-specific routing
- Volume Rules: Third priority for general distribution
- Default Fallback: Final safety net for all other cases
Testing and Validation
Pre-Deployment Testing
Sandbox Environment:- Test volume distribution with sample transactions
- Verify percentage calculations work correctly
- Confirm processor integration functions properly
- Compare performance with and without volume routing
- Test different percentage allocations
- Measure impact on success rates and costs
Go-Live Checklist
- Configuration validated and percentages total 100%
- All processors tested and confirmed working
- Monitoring alerts configured
- Team trained on new routing behavior
- Rollback plan prepared if issues arise
Support and Resources
Documentation:- Complete Smart Router documentation
- Processor-specific integration guides
- API reference documentation
- Dashboard help section
- Technical support team
- Community forums and best practices
Next Steps
After implementing Volume Based Routing:- Monitor Performance: Track distribution accuracy and processor performance
- Optimize Allocation: Adjust percentages based on performance data
- Expand Strategy: Consider additional routing rules for specific scenarios
- Cost Analysis: Regular review of processing costs and optimization opportunities
Summary
Volume Based Routing provides powerful traffic distribution capabilities that help optimize payment processing through:- Flexible percentage-based allocation across multiple processors
- Risk management through load distribution
- Cost optimization opportunities
- Easy configuration and management through the dashboard
- Integration with other routing strategies for comprehensive payment handling